BUNCHA SUNSANEEWITAYAKUL, M.D.
Medicine - Cardiology (Heart)
This website uses cookies 🍪
We use cookies to ensure you get the best online experience. For more details, please see our Privacy and Cookie Policy. Read more.


Have you ever felt it? A sudden heart palpitation like a drum roll, or feeling lightheaded as if you might faint even while sitting still. This might not just be stress, but a warning sign of "Atrial Fibrillation" or Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Learn about the condition and dive deep into heart ablation technologies that help treat a "fluttering heart" and restore a "normal rhythm."
Understand the disease and explore heart ablation technologies that restore your "fluttering heart" back to a "steady beat."
Normally, our heart has a "power plant" that sends signals for rhythmic contractions. In AF patients, stray electrical signals move chaotically, causing the upper chambers (atria) to "quiver" instead of beating normally, leading to inefficient blood circulation.
Initially, doctors may prescribe medication to control heart rhythm and prevent blood clots. However, lifelong medication may not be the ultimate answer, and some patients do not respond well to drugs. Catheter Ablation is an effective way to resolve the issue. Doctors insert a catheter into the heart to destroy the tissue causing abnormal electrical signals, allowing the heart to return to its normal rhythm. Currently, there are 3 notable ablation technologies:
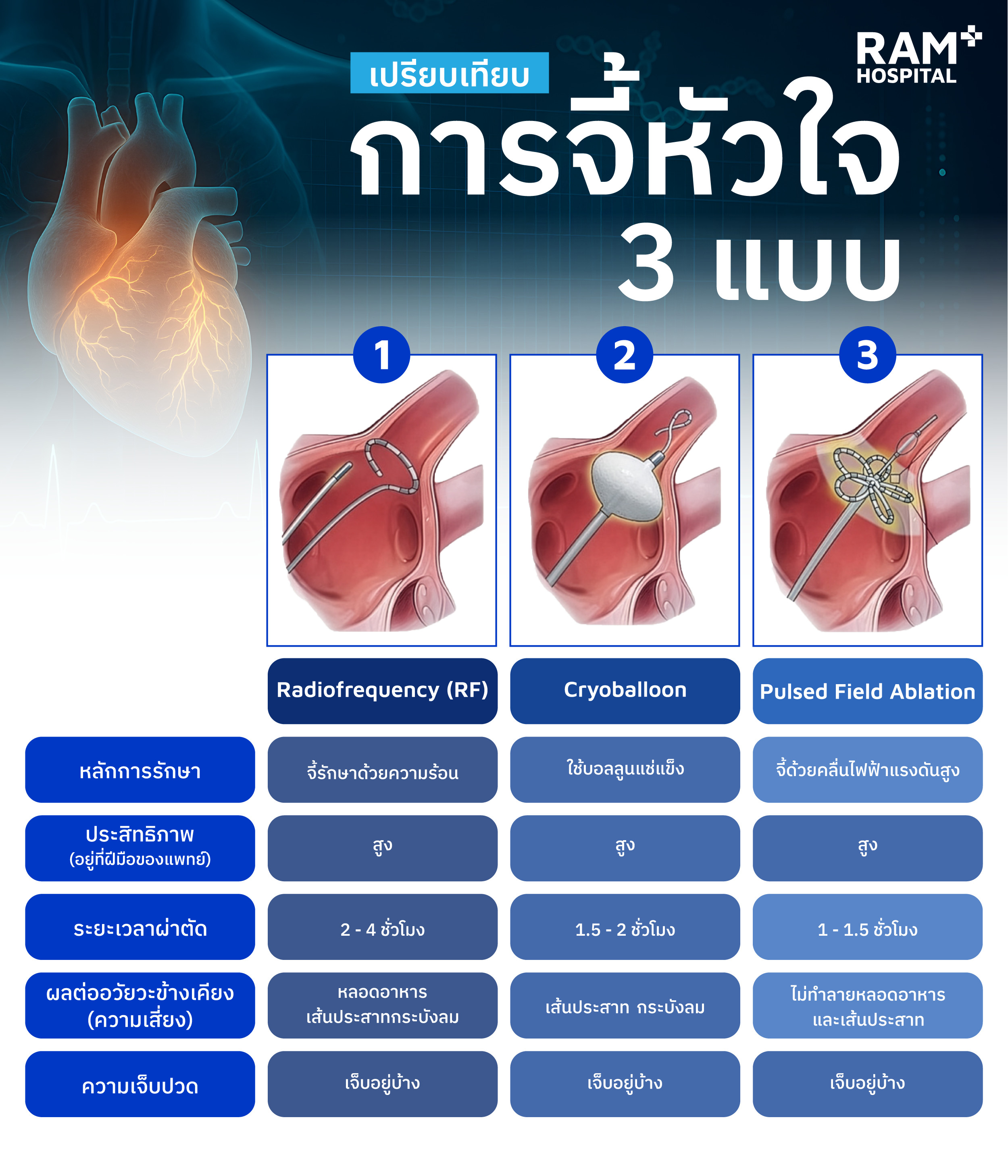
RF is the traditional standard method. Doctors use a catheter to deliver "Radiofrequency Heat" to cauterize abnormal points one by one to block electrical signals. The advantage is the ability to target any spot even in complex heart structures, allowing for customized treatment. However, it is time-consuming and may affect nearby organs if energy is not perfectly controlled.
This method was developed to reduce treatment time using a "Balloon filled with coolant." The balloon is inserted and inflated against the heart wall, releasing extreme cold (-40 to -50 degrees Celsius) to freeze heart tissue around the pulmonary veins, which are the primary source of AF. This method covers a large area at once, making it ideal for early-stage patients. However, since the balloon has a fixed shape, it may not be suitable for patients with highly irregular heart structures.
PFA uses short bursts of high-voltage electrical fields (microseconds) to create nano-sized pores in heart cells (Electroporation), causing them to dissipate naturally. The waves selectively target heart muscle cells without damaging nerves, the esophagus, or surrounding blood vessels, significantly shortening treatment time.
If you or your loved ones experience abnormal heart palpitations, do not ignore them. Consult a cardiologist promptly for an Electrocardiogram (ECG) and to plan the most appropriate treatment for a better quality of life and a healthy heart!
This article is for preliminary educational purposes only. Please consult a specialist for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Medicine - Cardiology (Heart)