PHOORIPAN ARAMWATANAPONG, M.D.
Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery
This website uses cookies 🍪
We use cookies to ensure you get the best online experience. For more details, please see our Privacy and Cookie Policy. Read more.


Parents are often concerned when their children suffer from chronic colds, loud snoring, or recurrent sore throats. These may not just be common health issues, but could be caused by "Tonsils and Adenoids" that are malfunctioning, becoming a reservoir for germs or obstructing the airway.
Tonsils and Adenoids are groups of lymphoid tissues responsible for trapping germs entering the body through the mouth and nose. Tonsils are located on the sides of the throat, while adenoids are located at the very top of the throat, behind the nasal cavity.
Normally, these glands are at their largest between the ages of 3-7, a period when the body is building immunity, and gradually shrink during adulthood. However, in some children, these glands can become chronically inflamed or abnormally enlarged, affecting their quality of life.
Medical professionals have clear indications for considering Tonsillectomy and Adenoidectomy to restore a patient's health, as follows:
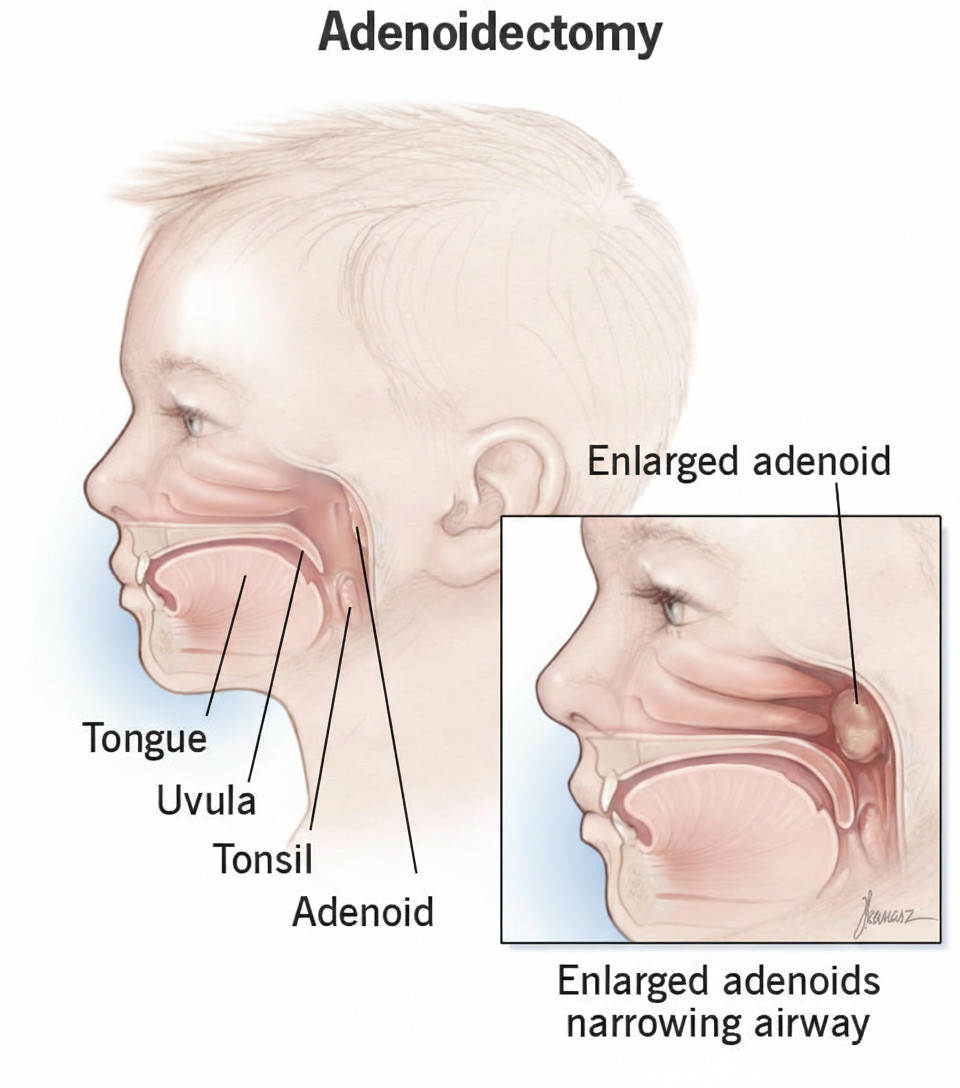
Ref: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/15447-adenoidectomy-adenoid-removal
Today, tonsil and adenoid surgery is no longer as concerning as in the past. With modern anesthetic and surgical technologies, such as Radiofrequency (RF) or Coblation, blood loss is minimal, trauma to surrounding tissue is reduced, and patients recover faster. The surgery takes only 30-45 minutes under professional medical care.
The key to rapid healing is post-operative care, especially during the first 1-2 weeks.
"Surgery is not always the first option. However, if there are clear indications, timely treatment will help children return to breathing easily, sleeping soundly, and growing up healthy and strong."
Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery